Parietal Lobe
"My brain doesn't like to be quiet." - Dan Fogler
Location
The parietal lobe is the middle section of the brain separated from the frontal lobe by the central sulcus. The location in the brain is indicated in the image below.
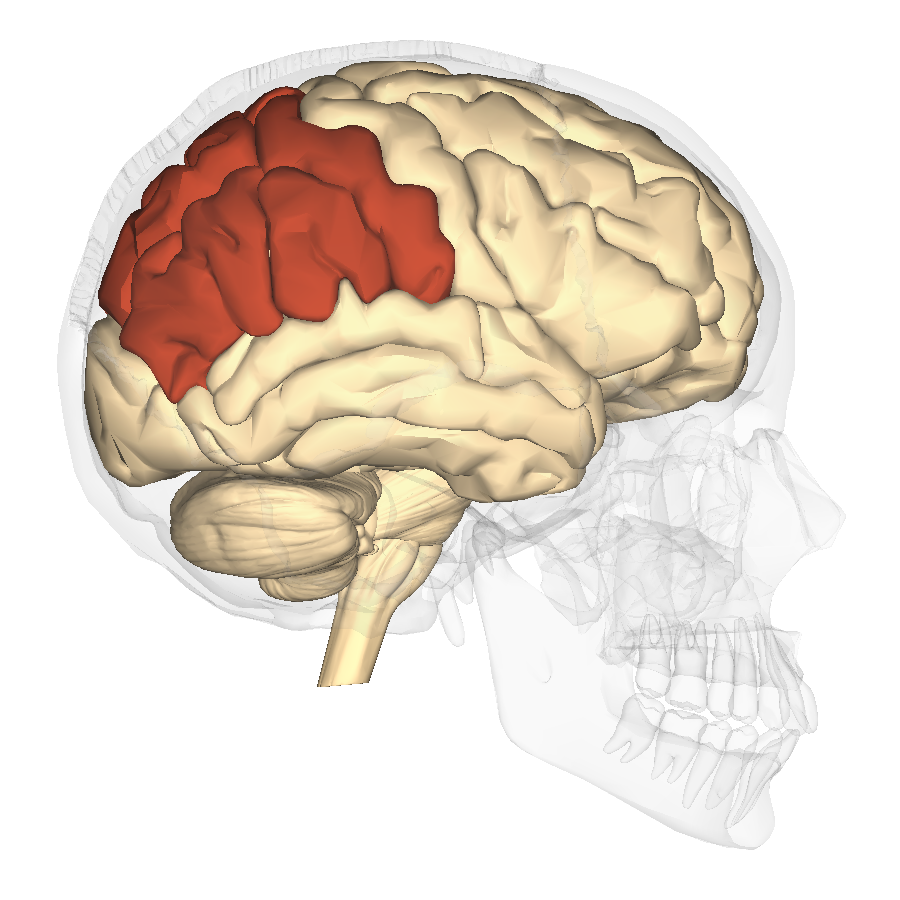
By Anatomography - en:Anatomography (setting page of this image), CC BY-SA 2.1 jp, Link
Functions
The parietal lobe houses the somatosensory cortex which is essential for processing sensual information from the body. Processing sensory information is the main function of the parietal lobe of the brain. This lobe processes information such as pressure, touch, temperature and pain that is being sensed in the body or by the body. processing here allows us to distinguish between one and two points of contact depending on the number of sensory receptors in that area. This is known as two-point discrimination.
Interesting Facts
An example of the workings of the parietal lobe is evident in a two-point discrimination test. Processing in the parietal lobe allows humans to distinguish between one and two points of contact. The parietal lobe processes the information that is being collected from changes in the distance between to points. At some point, two points begin to feel like one. The number of sensory receptors in an area will likely dictate how easily two points can be detected. With more receptors, mit is more likely for both points to be felt separately. However, over areas with fewer receptors, two points fairly far apart can feel like one because perhaps, only one receptor is noticing both points. All this information is being processed by the parietal lobe.